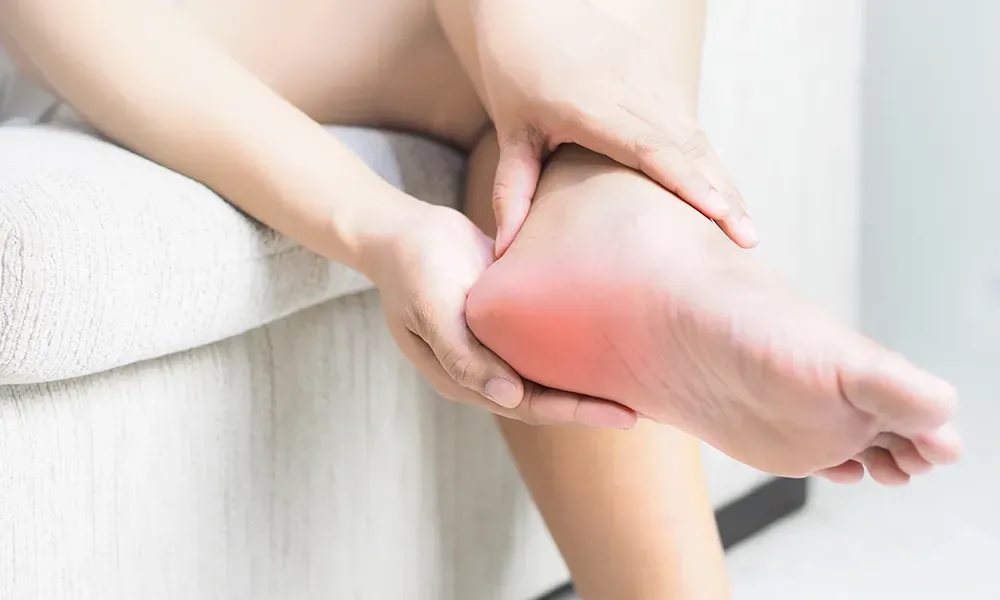
Chronic pain and swelling are common symptoms of many conditions, including arthritis, fibromyalgia, and autoimmune disorders. Inflammation is a key factor that contributes to these symptoms, and understanding the role of inflammation in chronic pain and swelling can help us better manage these conditions.
What is inflammation?
Inflammation is a natural process that occurs in response to injury, infection, or irritation. When tissues are damaged or infected, the body’s immune system responds by releasing chemicals that cause blood vessels to dilate, allowing immune cells to reach the affected area. This leads to redness, warmth, swelling, and pain.
While acute inflammation is a necessary part of the healing process, chronic inflammation can cause damage to tissues and organs over time. Chronic inflammation has been linked to a number of diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
The link between inflammation and chronic pain
Chronic pain is often associated with inflammation. Inflammatory chemicals such as cytokines and prostaglandins can sensitize nerve cells, making them more likely to fire in response to stimuli. This can lead to a condition known as hyperalgesia, where even mild stimuli can cause severe pain.
In addition to sensitizing nerve cells, inflammation can also cause structural changes in the nervous system. Chronic inflammation can lead to the formation of new neural pathways that perpetuate pain signals, even in the absence of ongoing tissue damage or inflammation.
The role of inflammation in swelling
Swelling, or edema, is another common symptom of inflammation. Inflammatory chemicals cause blood vessels to become more permeable, allowing fluid to leak into the surrounding tissues. This can lead to swelling and discomfort.
Chronic inflammation can also cause fibrosis, or the formation of scar tissue, which can interfere with the normal functioning of organs and tissues. This can lead to further swelling and pain.
Managing chronic pain and swelling
There are several strategies for managing chronic pain and swelling associated with inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin and ibuprofen can help reduce inflammation and pain, but they may have side effects such as stomach upset and increased risk of bleeding.
Other medications, such as corticosteroids and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), can also be effective in managing inflammation and reducing pain and swelling. However, these medications can have significant side effects and should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Lifestyle changes, such as exercise, weight management, and stress reduction, can also help manage chronic pain and swelling associated with inflammation. Physical therapy and alternative therapies such as acupuncture and massage may also be beneficial in reducing pain and improving function.
Inflammation plays a key role in chronic pain and swelling. Understanding the mechanisms of inflammation and how it contributes to these symptoms can help us develop more effective treatments for managing these conditions. By combining medication, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies, we can help reduce pain and swelling and improve overall quality of life for those with chronic pain and swelling.